
Electric Vehicle Safety and Maintenance: A Comprehensive Technical Guide
Introduction
The automotive industry is undergoing a revolutionary transformation with the rapid adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs). While EVs promise a greener future, they also introduce unique challenges in safety and maintenance. This guide aims to bridge the critical knowledge gap, equipping professionals with the technical insights needed to manage high-voltage systems safely and effectively.
1. Electrical Components
High-voltage cables and components can retain residual energy even after the system is powered down.
Exposure to electromagnetic fields and silent operation increases the risk of unnoticed activation2. Battery Systems
Damaged battery cells can lead to chemical exposure or thermal runaway, posing severe risks.
Batteries store immense energy, making improper handling potentially explosive.Risk Assessment and Safety Protocols
Emergency Response Procedures
Immediately assess the situation and establish a safety perimeter
Ensure the high-voltage system is isolated and de-energized.
Monitor for signs of thermal events, such as smoke or heat
Visual Inspection Protocols
Inspect high-voltage components for damage
Check the integrity of orange-colored cables, which indicate high-voltage systems
Assess battery containment and overall structural damage.
Vehicle Recovery Guidelines
Maintain a safe distance during recovery
Disconnect the 12/24V auxiliary system to prevent voltage generation
Avoid unauthorized towing, as this may activate regenerative braking systems.Maintenance and Repair Safety

Standard Operating ProceduresConduct a thorough visual inspection of high-voltage systems
Verify battery isolation before beginning repairs
Map high-voltage cables to prevent accidental contact
Required Safety Equipment: VDE 1000V Insulated Tools:

Specialized Battery Toolkit: We have especially designed an “Insulated Battery Toolkit” for safe handling and replacement of EV batteries.Learn more about Insulated Tools in the EV Industry
1. High-Voltage System Maintenance
Safety Requirements
Pre-Work Procedures
Isolate and lock out the high-voltage system.Discharge stored energy in capacitors.
Verify component status before proceeding.
Live Work Protocols
Follow manufacturer-specific guidelines.
Use personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves and face shields.
Professional Training Requirements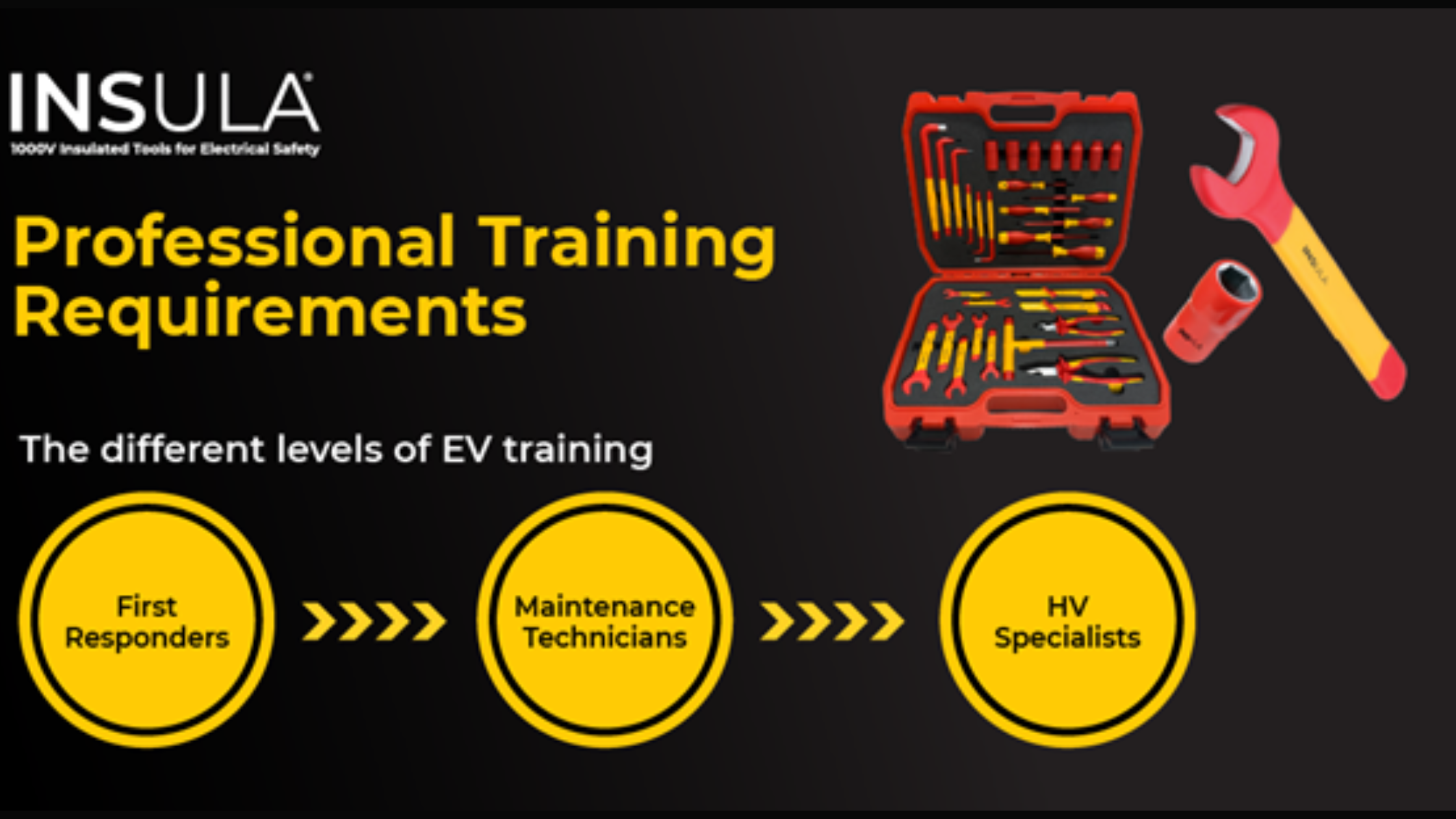
Skill Level Categories
First Responders
Focus on emergency assessment and initial isolation.Maintenance Technicians
Perform non-high-voltage repairs and diagnostic tests.
HV System Specialists
Handle advanced electrical maintenance and battery servicing.
Best Practices for EV Safety
General Safety GuidelinesAlways adhere to manufacturer specifications.
Use certified insulated tools.
Keep training certifications updated.
Emergency Response Protocol
Establish a safety perimeter.
Verify the high-voltage system is de-energized.
Continuously monitor for thermal events during emergencies.Technical Requirements
Essential Tools and Equipment
Insulated Tool Requirements
Basic Toolkit:


Conclusion
The evolution of EV technology underscores the importance of safety and technical expertise. Professionals must stay informed about manufacturer guidelines, utilize the right tools, and prioritize continuous education. By adhering to these principles, the risks associated with EV maintenance can be effectively mitigated.FAQs
1. What are the main safety risks of working with EVs?
High-voltage systems, chemical exposure, and thermal events pose significant risks.
2. How can professionals prepare for EV emergencies?By understanding isolation protocols, maintaining PPE, and staying updated on safety training.
3. What tools are essential for EV maintenance?VDE-insulated tools, battery diagnostic kits, and thermal imaging cameras are vital.
4. What training is required to work on high-voltage systems?Professionals need certifications in high-voltage safety and specialized maintenance training.
5. How often should EV safety procedures be reviewed?yearly, with updates aligned with technological advancements and manufacturer guidelines